Nanostructured Zinc-Nickel vs Conventional: 9x More Protection with Sapucaia's NanoGalv®
- Equipe - Sapucaia
- 5 de out. de 2025
- 2 min de leitura
Conventional Zinc-Nickel vs. Nanostructured Zinc-Nickel: What's the Difference?
In the automotive, solar energy, and oil & gas industries, zinc-nickel (Zn-Ni) coatings are widely used to extend the life of corrosion-prone parts and fasteners. However, there's a key difference that often goes unnoticed: traditional Zn-Ni is not the same as nanostructured Zn-Ni .
While the conventional process offers good protection, nanotechnology has brought a leap in performance with NanoGalv® , a coating developed by Modumetal and available in Brazil with application by Sapucaia .
What is Conventional Zinc-Nickel?
Traditional Zn-Ni is a homogeneous coating applied by electroplating. It meets automotive and industrial standards and offers corrosion resistance ranging from 500 to 1,500 hours in salt spray (depending on thickness and finish).
🔹 Main features:
Homogeneous Zn-Ni alloy with 12–16% nickel;
Need for thick layers (8–15 μm typical);
Good protection, but limited in extreme environments;
Uneven thickness in threads, corners and cavities;
Greater consumption of energy, metals and waste generation.
What is Nanostructured Zinc-Nickel (NanoGalv®)?
NanoGalv® is a Zn-Ni coating obtained through a patented nanostructured electrodeposition process.
Unlike conventional coatings, it does not form a homogeneous layer, but rather several overlapping nanometric layers that act as a multiple barrier against corrosion.
🔹 Main features of NanoGalv®:
Corrosion resistance up to 9x greater per unit thickness ;
Exceeds 3,000 hours in ASTM B117 salt spray with only 3–5 μm;
Low Hydrogen Embrittlement (LHE) process – reduces the risk of hydrogen embrittlement;
Better uniformity in critical areas such as threads and edges;
Up to 68% less waste and lower energy consumption ;
Direct replacement for conventional cadmium, zinc nickel and PTFE in critical oil & gas applications.
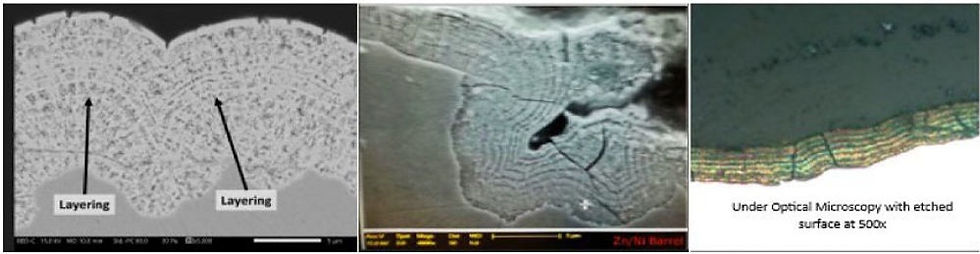
Direct Comparison
Feature | Conventional Zn-Ni | Nanostructured Zn-Ni (NanoGalv®) |
Structure | Homogeneous alloy | Overlapping nanometric layers |
Typical thickness | 8–15 μm | 3–5 μm |
Corrosion resistance (ASTM B117) | 500–1500 h | > 3,000 h |
Uniformity in geometries | Low | High |
Hydrogen embrittlement | Present risk | LHE Process (low risk) |
Sustainability | High consumption and waste | Up to 68% less waste and metals |
Why does this matter?
The choice between conventional Zn-Ni and nanostructured Zn-Ni can mean:
Longer component life;
Reduction of maintenance costs;
Lower environmental impact;
Better performance in critical sectors such as automotive, solar and oil & gas.
👉 Sapucaia is an authorized supplier of NanoGalv® in Brazil, bringing the most advanced corrosion protection technology to the national market.
🔗 Contact our team and find out how to apply nanostructured zinc-nickel to your projects.


